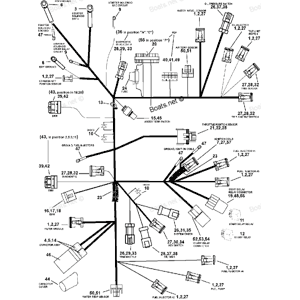
0514740 *CONNECTOR - 24 Socket EVINRUDE
E100FPLSOC, E100FPLSRS, E115FPLSDS, E115FPLSNF, E115FPLSOD, E115FPLSRE, E115FPLSTB, E115FPXSDS, E115FPXSOD, E115FPXSRE, E115FSLSDS, E135FCXSDE, E135FCXSNF, E135FCXSOB, E135FCXSRM, E135FCXSTA, E135FPLSDE, E135FPLSOB, E135FPLSRM, E135FPLSTA, E135FPLSTF
CONNECTOR

Price: query
Rating:
You can buy parts:
As an associate, we earn commssions on qualifying purchases through the links below
$306.03
04-07-2023
12.74[5.73] Pounds
-: -
DG PERFORMANCE 051-4740 Utility Series Slip-On Exhaust
Designed for maximum torque and power across torque curve || Made from durable 16 gauge steel body with a lightweight aluminum rear end cap || Features a "quiet" 86-92dB sound level and a removable 1" Quiet Core insert || Includes U.S.F.S. approved, removable screen-type spark arrestor; replacement spark arrestor sold separately
Designed for maximum torque and power across torque curve || Made from durable 16 gauge steel body with a lightweight aluminum rear end cap || Features a "quiet" 86-92dB sound level and a removable 1" Quiet Core insert || Includes U.S.F.S. approved, removable screen-type spark arrestor; replacement spark arrestor sold separately
Compatible models:
E100FPLSOC
E100FPLSRS
E115FPLSDS
E115FPLSNF
E115FPLSOD
E115FPLSRE
E115FPLSTB
E115FPXSDS
E115FPXSOD
E115FPXSRE
E115FSLSDS
E135FCXSDE
E135FCXSNF
E135FCXSOB
E135FCXSRM
E135FCXSTA
E135FPLSDE
E135FPLSOB
E135FPLSRM
E135FPLSTA
E135FPLSTF
E135FPXSDE
E135FPXSOB
E135FPXSRM
E135FSLSDE
E135FSLSTA
E135FSLSTF
E150FCXSDR
E150FCXSNF
E150FCXSOC
E150FCXSRS
E150FCXSTD
E150FHLSDR
E150FHLSOC
E150FHLSRS
E150FPLSDR
E150FPLSOC
E150FPLSRS
E150FPLSTD
E150FPLSTF
E150FPXSDR
E150FPXSOC
E150FPXSRS
E150FSLSDR
E150FSLSTF
E175FCXSDS
E175FCXSNF
E175FCXSOD
E175FCXSRE
E175FCXSTB
E175FPLSDS
E175FPLSOD
E175FPLSRE
E175FPLSTB
E175FPLSTF
E175FPXSDS
E175FPXSOD
E175FPXSRE
E175FSLSDD
E175FSLSTF
E175MFXSOS
E200FCXSNF
E200FCXSOE
E200FCXSRB
E200FCXSTM
E200FHLSOR
E200FHLSRC
E200FPLSNF
E200FPLSOE
E200FPLSRB
E200FPLSTM
E225FCXSNF
E225FCXSOE
E225FCXSRB
E225FCXSTM
E225FHLSOB
E225FHLSRM
E225FHLSTA
E225FPLSOE
E225FPLSRB
E250FCXSNF
E250FCXSOB
E250FCXSRM
E250FCXSTA
E250FPLSOM
E250FPLSRA
E250FPXSNF
E75FPLSNF
E75FPLSTA
E90FPLSNF
E90FPLSTB
EVINRUDE
BRP EVINRUDE entire parts catalog list:
- ENGINE ELECTRICAL HARNESS ASSEMBLY » 0514740
E115FPLSDS 2006
E115FPLSNF, E115FPXSNF 2002
E115FPLSOD, E115FSLSOD 2004,2005
E115FPLSRE, E115FSLSRE 2004
E115FPLSTB, E115FPXSTB, E115FSLSTB 2003
E115FPXSDS 2006
E115FPXSOD 2004,2005
E115FPXSRE 2004
E115FSLSDS 2006
E135FCXSDE 2006
E135FCXSNF, E135FPLSNF, E135FPXSNF 2002
E135FCXSOB 2004,2005
E135FCXSRM 2004
E135FCXSTA 2003
E135FPLSDE 2006
E135FPLSOB, E135FSLSOB 2004,2005
E135FPLSRM, E135FSLSRM 2004
E135FPLSTA, E135FPXSTA 2003
E135FPLSTF 2003
E135FPXSDE 2006
E135FPXSOB 2004,2005
E135FPXSRM 2004
E135FSLSDE 2006
E135FSLSTA 2003
E135FSLSTF 2003
E150FCXSDR 2006
E150FCXSNF, E150FPLSNF, E150FPXSNF 2002
E150FCXSOC 2004,2005
E150FCXSRS 2004
E150FCXSTD 2003
E150FHLSDR 2006
E150FHLSOC 2004,2005
E150FHLSRS 2004
E150FPLSDR 2006
E150FPLSOC, E150FSLSOC 2004,2005
E150FPLSRS, E150FSLSRS 2004
E150FPLSTD, E150FPXSTD, E150FSLSTD 2003
E150FPLSTF 2003
E150FPXSDR 2006
E150FPXSOC 2004,2005
E150FPXSRS 2004
E150FSLSDR 2006
E150FSLSTF 2003
E175FCXSDS 2006
E175FCXSNF, E175FPLSNF, E175FPXSNF 2002
E175FCXSOD 2004,2005
E175FCXSRE 2004
E175FCXSTB 2003
E175FPLSDS 2006
E175FPLSOD, E175FSLSOE 2004,2005
E175FPLSRE, E175FSLSRB 2004
E175FPLSTB, E175FPXSTB, E175FSLSTM 2003
E175FPLSTF 2003
E175FPXSDS 2006
E175FPXSOD 2004,2005
E175FPXSRE 2004
E175FSLSDD 2006
E175FSLSTF 2003
E175MFXSOS 2005
E175MFXSOS 2004
E200FCXSNF 2002
E200FCXSOE 2004,2005
E200FCXSRB 2004
E200FCXSTM, E200FHLSTS 2003
E200FHLSOR 2004,2005
E200FHLSRC 2004
E200FPLSNF, E200FPXSNF 2002
E200FPLSOE, E200FPXSOE, E200FSLSOE 2004,2005
E200FPLSRB, E200FPXSRB, E200FSLSRB 2004
E200FPLSTM, E200FPXSTM, E200FSLSTM 2003
E225FCXSNF, E225FCZSNF, E225FHLSNF, E225FPLSNF, E225FPXSNF, E225FPZSNF 2002
E225FCXSOE, E225FCZSOE 2004,2005
E225FCXSRB, E225FCZSRB 2004
E225FCXSTM, E225FCZSTM, E225FPLSTM, E225FPXSTM, E225FPZSTM 2003
E225FHLSOB, E225FHXSOC 2004,2005
E225FHLSRM, E225FHXSRS 2004
E225FHLSTA 2003
E225FPLSOE, E225FPXSOE, E225FPZSOE 2004,2005
E225FPLSRB, E225FPXSRB, E225FPZSRB 2004
E250FCXSNF, E250FCZSNF, E250FPZSNF 2002
E250FCXSOB, E250FCZSOB 2004,2005
E250FCXSRM, E250FCZSRM 2004
E250FCXSTA, E250FCZSTA, E250FPLSTR, E250FPXSTA, E250FPZSTA 2003
E250FPLSOM, E250FPXSOB, E250FPZSOB 2004,2005
E250FPLSRA, E250FPXSRM, E250FPZSRM 2004
E250FPXSNF 2002
E75FPLSNF 2002
E75FPLSTA 2003
E90FPLSNF 2002
E90FPLSTB, E90FSLSTB 2003
Information:
Engine Design
Cylinder And Valve LocationBore ... 120.7 mm (4.75 in)Stroke ... 152.4 mm (6.00 in)Number of Cylinders ... 6Cylinder Arrangement ... in lineValves per Cylinder ... 2Combustion ... Direct InjectionFiring Order (Injection Sequence) ... 1, 5, 3, 6, 2, 4Rotation of Crankshaft (when viewed from flywheel end) ... counterclockwise The No. 1 cylinder is opposite the flywheel end.Fuel System
Fuel Flow
Fuel System Schematic
(1) Fuel tank. (2) Fuel return line. (3) Priming pump. (4) Fuel injection nozzle. (5) Fuel injection line. (6) Fuel injection pump. (7) Primary fuel filter. (8) Check valves. (9) Fuel transfer pump. (10) Secondary fuel filter. (11) Constant bleed valve. (12) Fuel injection pump housing.Fuel is pulled from fuel tank (1) through primary fuel filter (7) and check valves (8) by fuel transfer pump (9). From the fuel transfer pump the fuel is pushed through secondary fuel filter (10) and to the fuel manifold in fuel injection pump housing (12). A bypass valve in the fuel transfer pump keeps the fuel pressure in the system at 170 to 280 kPa (25 to 40 psi). Constant bleed valve (11) lets a constant flow of fuel go through fuel return line (2) back to fuel tank (1). The constant bleed valve returns approximately 34 liters (9 gal) per hour of fuel and air to the fuel tank. This helps keep the fuel cool and free of air. Fuel injection pump (6) gets fuel from the fuel manifold and pushes fuel at very high pressure through fuel injection line (5) to fuel injection nozzle (4).The fuel injection nozzle has very small holes in the tip that change the flow of fuel to a very fine spray that gives good fuel combustion in the cylinder.Fuel Injection Pump
The fuel injection pump increases the pressure of the fuel and sends an exact amount of fuel to the fuel injection nozzle. There is one fuel injection pump for each cylinder in the engine.
Fuel Injection Pump
(1) Inlet passage. (2) Check valve. (3) Bypass closed port. (4) Spill port. (5) Scroll. (6) Slot. (7) Pump plunger. (8) Spring. (9) Fuel rack. (10) Gear. (11) Lifter. (12) Cam lobe.The fuel injection pump is moved by cam lobe (12) of the fuel pump camshaft. When the camshaft turns, the cam lobe raises lifter (11) and pump plunger (7) to the top of the stroke. The pump plunger always makes a full stroke. As the camshaft turns farther, spring (8) returns the pump plunger and lifter to the bottom of the stroke.When the pump plunger is at the bottom of the stroke, fuel transfer pump pressure goes into inlet passage (1), around the pump barrel and to bypass closed port (3). Fuel fills the area above the pump plunger.After the pump plunger begins the up stroke, fuel will be pushed out the bypass closed port until the top of the pump plunger closes the port. As the pump plunger travels farther up, the pressure of the fuel increases. At approximately 690 kPa (100 psi), check valve (2) opens and lets fuel flow into the fuel injection line to the fuel injection nozzle. When the pump plunger travels farther up, scroll (5) uncovers spill port (4). The fuel above the pump plunger goes through slot (6), along the edge of scroll (5) and out spill port (4) back to the fuel manifold. This is the end of the injection stroke. The pump plunger can have more travel up, but no more fuel will be sent to the fuel injection nozzle.When the pump plunger travels down and uncovers bypass closed port (3), fuel begins to fill the area above the pump plunger again, and the pump is ready to begin another stroke.The amount of fuel the injection pump sends to the injection nozzle is changed by the rotation of the pump plunger. Gear (10) is attached to the pump plunger and is in mesh with fuel rack (9). The governor moves the fuel rack according to the fuel needs of the engine. When the governor moves the fuel rack, and the fuel rack turns the pump plunger, scroll (5) changes the distance the pump plunger pushes fuel between bypass closed port (3) and spill port (4) opening. The longer the distance from the top of the pump plunger to the point where scroll (5) uncovers spill port (4), the more fuel will be injected.To stop the engine, the pump plunger is rotated so that slot (6) on the pump plunger is in line with spill port (4). The fuel will now go out the spill port and not to the injection nozzle.Fuel Injection Nozzle
The fuel injection nozzle goes through the cylinder head into the combustion chamber. The fuel injection pump sends fuel with high pressure to the fuel injection nozzle where the fuel is made into a fine spray for good combustion.
Fuel Injection Nozzle
(1) Carbon dam. (2) Seal. (3) Passage. (4) Filter screen. (5) Orifices. (6) Valve. (7) Diameter. (8) Spring.Seal (2) goes against the cylinder head and prevents leakage of compression from the cylinder. Carbon dam (1) keeps carbon out of the bore in the cylinder head for the fuel injection nozzle.Fuel with high pressure from the fuel injection pump goes into the inlet passage. Fuel then goes through filter screen (4) and into passage (3) to the area below diameter (7) of valve (6). When the pressure of the fuel that pushes against diameter (7) becomes greater than the force of spring (8), valve (6) lifts up. This occurs when the fuel pressure goes above the Valve Opening Pressure of the fuel injection nozzle. When valve (6) lifts, the tip of the valve comes off the fuel injection nozzle seat and the fuel will go through orifices (5) into the combustion chamber.The injection of fuel continues until the pressure of fuel against diameter (7) becomes less than the force of spring (8). With less pressure against diameter (7), spring (8) pushes valve (6) against the fuel injection nozzle seat and
Cylinder And Valve LocationBore ... 120.7 mm (4.75 in)Stroke ... 152.4 mm (6.00 in)Number of Cylinders ... 6Cylinder Arrangement ... in lineValves per Cylinder ... 2Combustion ... Direct InjectionFiring Order (Injection Sequence) ... 1, 5, 3, 6, 2, 4Rotation of Crankshaft (when viewed from flywheel end) ... counterclockwise The No. 1 cylinder is opposite the flywheel end.Fuel System
Fuel Flow
Fuel System Schematic
(1) Fuel tank. (2) Fuel return line. (3) Priming pump. (4) Fuel injection nozzle. (5) Fuel injection line. (6) Fuel injection pump. (7) Primary fuel filter. (8) Check valves. (9) Fuel transfer pump. (10) Secondary fuel filter. (11) Constant bleed valve. (12) Fuel injection pump housing.Fuel is pulled from fuel tank (1) through primary fuel filter (7) and check valves (8) by fuel transfer pump (9). From the fuel transfer pump the fuel is pushed through secondary fuel filter (10) and to the fuel manifold in fuel injection pump housing (12). A bypass valve in the fuel transfer pump keeps the fuel pressure in the system at 170 to 280 kPa (25 to 40 psi). Constant bleed valve (11) lets a constant flow of fuel go through fuel return line (2) back to fuel tank (1). The constant bleed valve returns approximately 34 liters (9 gal) per hour of fuel and air to the fuel tank. This helps keep the fuel cool and free of air. Fuel injection pump (6) gets fuel from the fuel manifold and pushes fuel at very high pressure through fuel injection line (5) to fuel injection nozzle (4).The fuel injection nozzle has very small holes in the tip that change the flow of fuel to a very fine spray that gives good fuel combustion in the cylinder.Fuel Injection Pump
The fuel injection pump increases the pressure of the fuel and sends an exact amount of fuel to the fuel injection nozzle. There is one fuel injection pump for each cylinder in the engine.
Fuel Injection Pump
(1) Inlet passage. (2) Check valve. (3) Bypass closed port. (4) Spill port. (5) Scroll. (6) Slot. (7) Pump plunger. (8) Spring. (9) Fuel rack. (10) Gear. (11) Lifter. (12) Cam lobe.The fuel injection pump is moved by cam lobe (12) of the fuel pump camshaft. When the camshaft turns, the cam lobe raises lifter (11) and pump plunger (7) to the top of the stroke. The pump plunger always makes a full stroke. As the camshaft turns farther, spring (8) returns the pump plunger and lifter to the bottom of the stroke.When the pump plunger is at the bottom of the stroke, fuel transfer pump pressure goes into inlet passage (1), around the pump barrel and to bypass closed port (3). Fuel fills the area above the pump plunger.After the pump plunger begins the up stroke, fuel will be pushed out the bypass closed port until the top of the pump plunger closes the port. As the pump plunger travels farther up, the pressure of the fuel increases. At approximately 690 kPa (100 psi), check valve (2) opens and lets fuel flow into the fuel injection line to the fuel injection nozzle. When the pump plunger travels farther up, scroll (5) uncovers spill port (4). The fuel above the pump plunger goes through slot (6), along the edge of scroll (5) and out spill port (4) back to the fuel manifold. This is the end of the injection stroke. The pump plunger can have more travel up, but no more fuel will be sent to the fuel injection nozzle.When the pump plunger travels down and uncovers bypass closed port (3), fuel begins to fill the area above the pump plunger again, and the pump is ready to begin another stroke.The amount of fuel the injection pump sends to the injection nozzle is changed by the rotation of the pump plunger. Gear (10) is attached to the pump plunger and is in mesh with fuel rack (9). The governor moves the fuel rack according to the fuel needs of the engine. When the governor moves the fuel rack, and the fuel rack turns the pump plunger, scroll (5) changes the distance the pump plunger pushes fuel between bypass closed port (3) and spill port (4) opening. The longer the distance from the top of the pump plunger to the point where scroll (5) uncovers spill port (4), the more fuel will be injected.To stop the engine, the pump plunger is rotated so that slot (6) on the pump plunger is in line with spill port (4). The fuel will now go out the spill port and not to the injection nozzle.Fuel Injection Nozzle
The fuel injection nozzle goes through the cylinder head into the combustion chamber. The fuel injection pump sends fuel with high pressure to the fuel injection nozzle where the fuel is made into a fine spray for good combustion.
Fuel Injection Nozzle
(1) Carbon dam. (2) Seal. (3) Passage. (4) Filter screen. (5) Orifices. (6) Valve. (7) Diameter. (8) Spring.Seal (2) goes against the cylinder head and prevents leakage of compression from the cylinder. Carbon dam (1) keeps carbon out of the bore in the cylinder head for the fuel injection nozzle.Fuel with high pressure from the fuel injection pump goes into the inlet passage. Fuel then goes through filter screen (4) and into passage (3) to the area below diameter (7) of valve (6). When the pressure of the fuel that pushes against diameter (7) becomes greater than the force of spring (8), valve (6) lifts up. This occurs when the fuel pressure goes above the Valve Opening Pressure of the fuel injection nozzle. When valve (6) lifts, the tip of the valve comes off the fuel injection nozzle seat and the fuel will go through orifices (5) into the combustion chamber.The injection of fuel continues until the pressure of fuel against diameter (7) becomes less than the force of spring (8). With less pressure against diameter (7), spring (8) pushes valve (6) against the fuel injection nozzle seat and
Parts connector EVINRUDE:
0511866
0511866 . CONNECTOR
BE115TLEDA, BE130TLECE, BE130TLEDM, BE130TLEUB, C155WTLM, CE275TLCDC, CE275TLCOS, CE300TLCDC, CE300TLCOS, E100FPLSOC, E100FPLSRS, E100STLCCA, E100STLCEM, E100STLEIE, E100STLEND, E100STLERC, E100STLESB, E100STLETS, E100WMLCDR, E100WMLCOC, E100WMLCRS,
0513357

0513357 CONNECTOR
BE10FAEDC, BE10FAEUR, BE10FDLECM, BE10FDLEDR, BE10FDLEUA, BE115ELEDR, BE115ELEUA, BE115GLECM, BE115TLEDA, BE130TLECE, BE130TLEDM, BE130TLEUB, BE150ELECD, BE150ELEDB, BE150ELEUC, BE15FAEDR, BE15FAEUA, BE15FDLECM, BE175EXECD, BE175EXEDB, BE175EXEUC, BE
0513356

0513356 CONNECTOR
BE10FAEDC, BE10FAEUR, BE10FDLECM, BE10FDLEDR, BE10FDLEUA, BE115ELEDR, BE115ELEUA, BE115GLECM, BE115TLEDA, BE130TLECE, BE130TLEDM, BE130TLEUB, BE150ELECD, BE150ELEDB, BE150ELEUC, BE15FAEDR, BE15FAEUA, BE15FDLECM, BE175EXECD, BE175EXEDB, BE175EXEUC, BE
0513663

0513663 CONNECTOR
BE10FDLECM, BE10FDLEDR, BE10FDLEUA, BE115ELEDR, BE115ELEUA, BE115GLECM, BE115TLEDA, BE130TLECE, BE130TLEDM, BE130TLEUB, BE150ELECD, BE150ELEDB, BE150ELEUC, BE15FAEDR, BE15FAEUA, BE15FDLECM, BE175EXECD, BE175EXEDB, BE175EXEUC, BE200CXECM, BE200CXEDR,
3010124
3010124 CONNECTOR, 2-pin, air temp.
E100FPLSOC, E100FPLSRS, E115DBXSUC, E115DPLSUC, E115DPXSUC, E115DSLSUC, E115FPLEEC, E115FPLSDS, E115FPLSIF, E115FPLSNF, E115FPLSOD, E115FPLSRE, E115FPLSSH, E115FPLSTB, E115FPXSDS, E115FPXSOD, E115FPXSRE, E115FSLECS, E115FSLSDS, E135FCXSDE, E135FCXSIF
3010049

3010049 CONNECTOR, Motor not serviced
DE150CXAAA, DE150CXAAC, DE150CXINS, DE150PXAAA, DE150PXAAC, DE150PXINS, DE200CXAAA, DE200CXAAC, DE200HXAAA, DE200HXAAC, DE200HXAAD, DE200PXAAA, DE200PXAAC, DE200XCAAA, DE200XCAAC, DE200XCAAD, DE225CXAAA, DE225CXAAC, DE225CXAAD, DE225CXINS, DE225PXAAA
0514591
0514591 CONNECTOR, TPS
E100FPLSOC, E100FPLSRS, E115FPLEEC, E115FPLSDS, E115FPLSIF, E115FPLSNF, E115FPLSOD, E115FPLSRE, E115FPLSSH, E115FPLSTB, E115FPXSDS, E115FPXSOD, E115FPXSRE, E115FSLECS, E115FSLSDS, E135FCXSDE, E135FCXSIF, E135FCXSNF, E135FCXSOB, E135FCXSRM, E135FCXSSS
3010593
3010593 CONNECTOR, 2-pin
E200FCSSSC, E200FCXEEN, E200FCXSIF, E200FCXSNF, E200FCXSOE, E200FCXSRB, E200FCXSTM, E200FHLSOR, E200FHLSRC, E200FPLSNF, E200FPLSOE, E200FPLSRB, E200FPLSSC, E200FPLSTM, E200FPXSSC, E225FCXEEN, E225FCXSIF, E225FCXSNF, E225FCXSOE, E225FCXSRB, E225FCXSSC